How to measure roast level?
In a previous article, I introduced the eight levels of roasting, but I also mentioned that they are just a guideline.
This does not mean that there are no methods to objectively measure the degree of roasting.
A commonly used method is to measure the ``color'' of roasted beans.
Of course, since the evaluation is based on the appearance, we cannot tell about the degree of burntness inside the coffee beans.
However, it is possible to determine the degree of roasting by comparing the color.
This does not mean that there are no methods to objectively measure the degree of roasting.
A commonly used method is to measure the ``color'' of roasted beans.
Of course, since the evaluation is based on the appearance, we cannot tell about the degree of burntness inside the coffee beans.
However, it is possible to determine the degree of roasting by comparing the color.
“Agtron value” used in SCA cupping
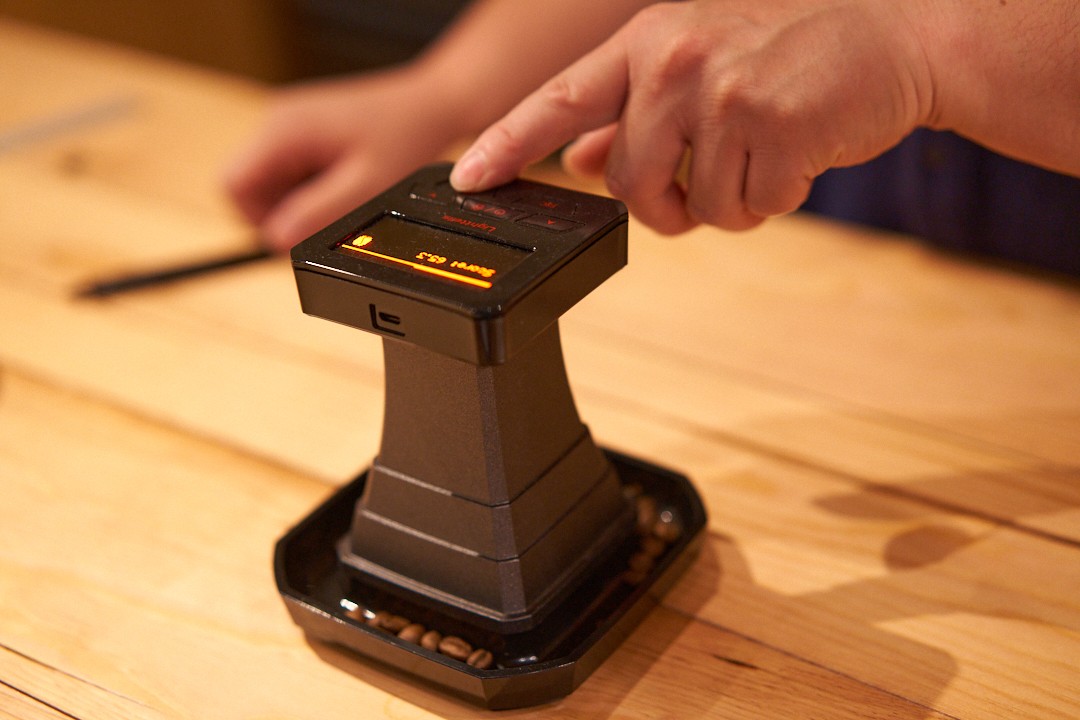

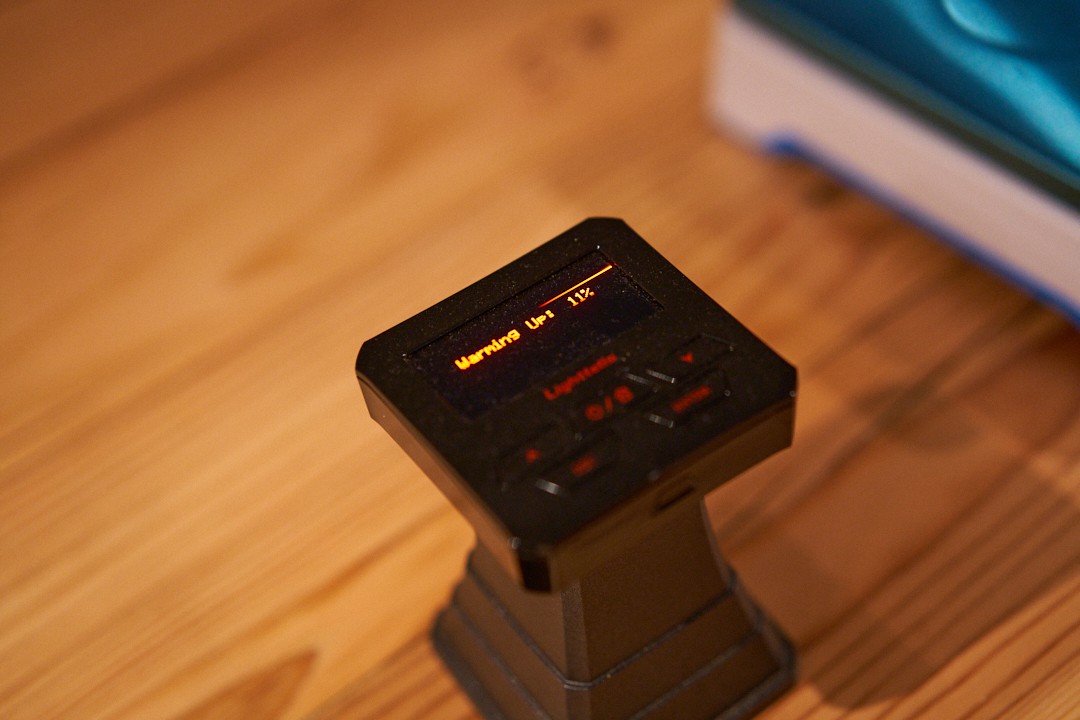
The SCA (Specially Coffee Association) uses numerical values such as Agtron (Agtron Gourmet Color Scale) in its cupping regulations.
Agtron is a food Hikaru Hikaru meter released by Agtron, Inc. in the United States, which uses near-infrared rays to determine the color of roasted beans.
That number is also called the "Agtron number."
As for measuring equipment, products from Lighttells, which can measure the same numerical value as the Agtron number, are also commonly used in Japan.
Here I will give an example of the correspondence between the Agtron value and the degree of roasting, but it is just an example, so I hope you can think of it as an example to help you understand the relationship: if the value is large, it is light roasted, and if it is small, it is dark roasted. think.
Roast degree and Agtron value
Light roast: 80-70
Cinnamon roast: 70-58
Medium roast: 58-50
High roast: 50-45
City roast: 45-40
Full City Roast: 40-35
French roast: 35-25
Italian roast: less than 25
Cinnamon roast: 70-58
Medium roast: 58-50
High roast: 50-45
City roast: 45-40
Full City Roast: 40-35
French roast: 35-25
Italian roast: less than 25
What is the "L value" used in Japan?

On the other hand, in Japan, the "L value" is used to express the degree of roasting as an objective numerical value. The "L value" is the value measured using a color difference meter to measure the brightness of the powder ground in a mill.
The L value is the "L" value that represents brightness in the Lab standard set by the International Commission on Illumination, and the L value for black = 0 and the L value for white = 100.
However, since the L value is a value that varies depending on the values of "a" and "b", which represent the hue, it is better to consider this value as a reference value only.
The All Japan Coffee Association's certification book introduces it as follows (it is also expressed as reference L value in the textbook).
The L value is the "L" value that represents brightness in the Lab standard set by the International Commission on Illumination, and the L value for black = 0 and the L value for white = 100.
However, since the L value is a value that varies depending on the values of "a" and "b", which represent the hue, it is better to consider this value as a reference value only.
The All Japan Coffee Association's certification book introduces it as follows (it is also expressed as reference L value in the textbook).
Roast degree and reference L value
Light roast: 27.0 or more Cinnamon roast: 25.0 or more but less than 27.0 Medium roast: 22.5 or more but less than 25.0 High roast: 20.5 or more but less than 22.5 City roast: 18.5 or more but less than 20.5 Full city roast: 16.5 or more but less than 18.5 French roast: 15.0 or more but less than 16.5
Italian roast: less than 15.0
In this way, for both numbers, the higher the value, the lighter the degree of roasting.
If the degree of roasting is determined numerically, variations can be suppressed and it is useful for comparison.
So far, we have talked about how to judge the degree of roasting based on numerical values.
If the degree of roasting is determined numerically, variations can be suppressed and it is useful for comparison.
So far, we have talked about how to judge the degree of roasting based on numerical values.
We will discuss roast level in more detail in a future article.
2024.1.18
CROWD ROASTER